Crohn’s Disease: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction
Crohn’s Disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, impacting millions of people worldwide. This complex disease is part of a group of conditions known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and can significantly alter a person’s quality of life. Despite its prevalence, Crohn’s Disease remains shrouded in mystery and poses considerable challenges for both patients and healthcare providers.
The journey to understanding Crohn’s Disease involves exploring its multifaceted nature—from the varied symptoms and diagnostic hurdles to the diverse treatment options available. This article aims to unravel the complexities of Crohn’s Disease, offering a comprehensive guide to help patients, families, and even curious readers gain a deeper insight into managing this condition. Read on to discover everything you need to know about Crohn’s Disease, from its early warning signs to the latest in treatment advancements.
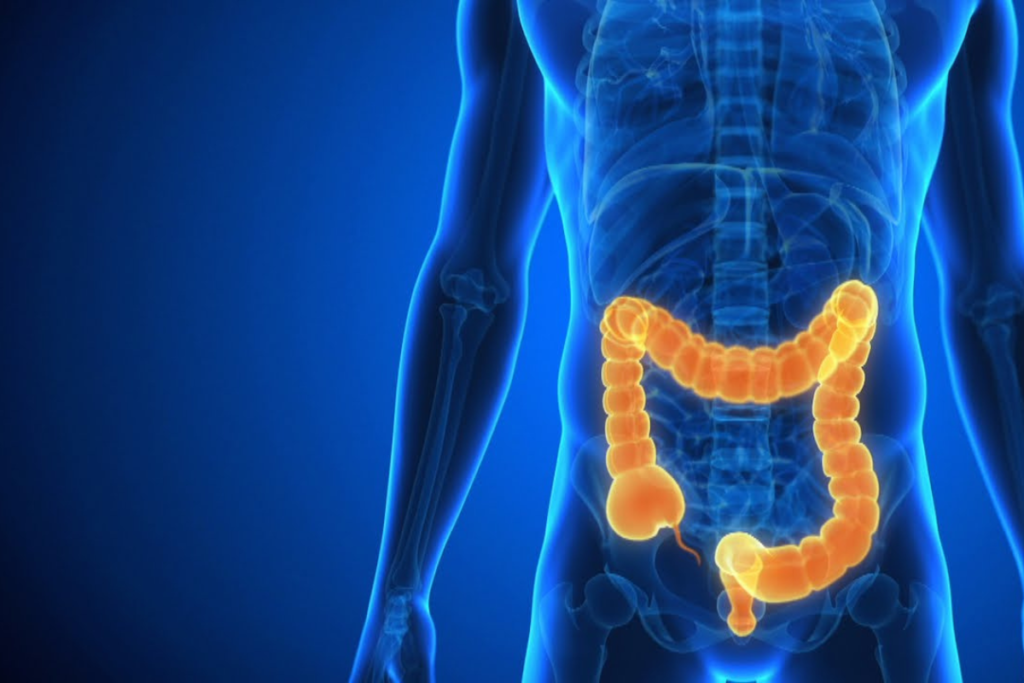
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s Disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. The inflammation associated with Crohn’s can penetrate deep into the layers of the bowel tissue, causing a variety of symptoms and complications. Unlike ulcerative colitis, which is limited to the colon, Crohn’s Disease can affect multiple areas of the GI tract, often in a patchy distribution.
The exact cause of Crohn’s Disease remains unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, as the disease tends to run in families. Environmental factors, such as diet, smoking, and stress, can also trigger or exacerbate the condition. Moreover, an abnormal immune response to gut bacteria is thought to contribute to the chronic inflammation seen in Crohn’s Disease.
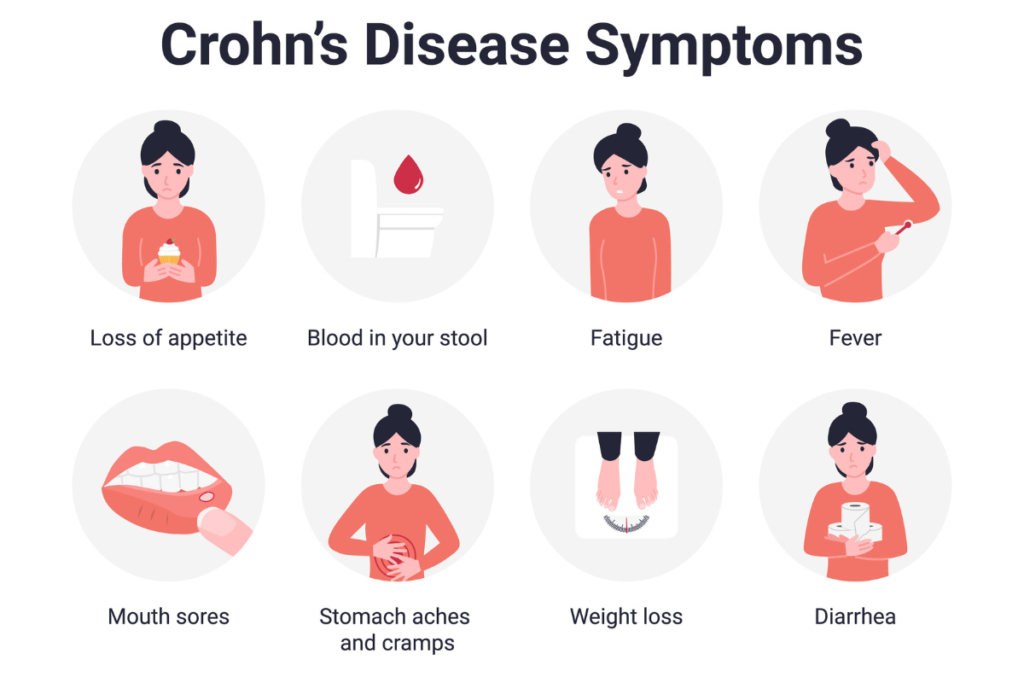
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
The symptoms of Crohn’s Disease can vary widely among individuals, depending on the severity and location of the inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain and Cramping: Persistent abdominal pain and cramping are hallmark symptoms of Crohn’s Disease, often resulting from inflammation and ulceration in the GI tract.
- Chronic Diarrhea: Frequent diarrhea is a common issue, which can lead to dehydration and nutrient deficiencies.
- Weight Loss and Malnutrition: Inflammation in the intestines can interfere with nutrient absorption, leading to unintended weight loss and malnutrition.
- Fatigue: Chronic inflammation and the body’s ongoing battle with the disease often lead to fatigue and a general sense of being unwell.
- Fever: Some individuals may experience fever during flare-ups.
- Blood in Stool: Rectal bleeding can occur due to ulcers or inflammation in the GI tract.
- Reduced Appetite: Pain and discomfort can lead to a decreased desire to eat, exacerbating nutritional deficiencies.
These symptoms can come and go, with periods of remission interspersed with flare-ups. The unpredictability of symptom severity and timing can make living with Crohn’s Disease particularly challenging.
Diagnosing Crohn’s Disease
Diagnosing Crohn’s Disease can be complex due to its similarity to other gastrointestinal disorders. A comprehensive evaluation typically involves multiple steps:
Medical History and Physical Examination
The diagnostic process begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, family history of IBD, and any potential environmental or lifestyle factors that could contribute to the condition.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests, including blood tests and stool samples, are used to look for signs of inflammation, infection, and anemia. Elevated levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) can indicate the presence of inflammation. Stool tests can help rule out infections and identify inflammation markers in the intestines.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are crucial for visualizing the extent and location of inflammation in the GI tract. Common imaging techniques include:
- Endoscopy and Colonoscopy: These procedures involve using a flexible tube with a camera to examine the inner lining of the GI tract. Biopsies can be taken during these procedures for further analysis.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: These scans provide detailed images of the intestines and can help identify areas of inflammation, strictures, and fistulas.
- Capsule Endoscopy: In some cases, a small capsule with a camera is swallowed, which takes images of the small intestine as it passes through.
Differential Diagnosis
Because Crohn’s Disease shares symptoms with other GI disorders, such as ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), differential diagnosis is essential. This process involves ruling out other conditions to confirm a diagnosis of Crohn’s Disease.
Treatment Options for Crohn’s Disease
While there is currently no cure for, various treatment options can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and maintain remission. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual’s specific condition and may include a combination of medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications.
Medications
Medications are the cornerstone of Crohn’s Disease treatment. The choice of medication depends on the severity of the disease and the patient’s response to previous treatments. Commonly used medications include:
- Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Corticosteroids and aminosalicylates are often prescribed to reduce inflammation in the GI tract.
- Immune System Suppressors: Medications like azathioprine, methotrexate, and mercaptopurine help suppress the immune response that causes inflammation.
- Biologics: These are newer drugs that target specific proteins involved in the inflammatory process. Examples include infliximab, adalimumab, and ustekinumab.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat or prevent infections in the intestines.
Diet and Nutrition
Proper nutrition is crucial for managing Crohn’s Disease. Patients may need to adjust their diets to avoid foods that trigger symptoms and ensure they receive adequate nutrients. A registered dietitian can help create a personalized nutrition plan. Some dietary recommendations include:
- Low-Fiber Diets: During flare-ups, a low-fiber diet may help reduce symptoms by minimizing irritation in the intestines.
- Nutritional Supplements: Vitamin and mineral supplements may be necessary to address deficiencies caused by malabsorption.
- Small, Frequent Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help manage symptoms and improve nutrient absorption.
Surgery
Surgery is often considered when medications and dietary changes do not provide sufficient relief. Surgical options include:
- Resection: Removing the damaged section of the intestine and reconnecting the healthy ends.
- Strictureplasty: Widening narrow sections of the intestine without removing any part of it.
- Abscess Drainage and Fistula Repair: Addressing complications such as abscesses and fistulas.
Surgery can provide significant symptom relief, but it is not a cure, and recurrence of the disease is common.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments and dietary adjustments, certain lifestyle changes can help manage Crohn’s Disease:
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so stress reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, and counseling can be beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve overall health and reduce stress.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking has been linked to increased severity of Crohn’s Disease symptoms, so quitting smoking is highly recommended.
Living with Crohn’s Disease
Living with Crohn’s Disease requires ongoing management and support. Patients must work closely with their healthcare team to develop a comprehensive treatment plan. Support from family, friends, and support groups can also provide invaluable emotional and practical assistance.
Mental Health
Chronic illnesses like Crohn’s Disease can significantly impact mental health. Patients should seek support for anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. Therapy, support groups, and mindfulness practices can be valuable resources for maintaining mental well-being.
Regular Monitoring
Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential for managing Crohn’s Disease effectively. Patients should stay informed about their condition and communicate any changes in symptoms to their healthcare providers promptly. This proactive approach helps in adjusting treatment plans as needed and addressing any complications early.
Education and Advocacy
Understanding the disease and advocating for oneself is crucial. Patients should educate themselves about Crohn’s Disease, stay updated on new research and treatments, and advocate for better healthcare resources and support. Being an informed patient empowers individuals to make better decisions about their health and treatment options.
Conclusion
Crohn’s Disease is a complex and challenging condition that requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to management. While there is no cure, advancements in treatment and a better understanding of the disease have significantly improved the outlook for patients. By staying informed, seeking appropriate medical care, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, individuals with Crohn’s Disease can lead active and fulfilling lives.
Understanding and managing Crohn’s Disease is a continuous journey that involves patience, resilience, and support. As research progresses and new treatments emerge, there is hope for even better outcomes and a higher quality of life for those affected by this condition. If you or a loved one is living with Crohn’s Disease, remember that you are not alone, and there are resources and support available to help you navigate this journey.
In conclusion, Crohn’s Disease may pose significant challenges, but with the right knowledge, treatment, and support, patients can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Stay informed, stay proactive, and never hesitate to seek help and support from healthcare providers and support networks. Together, we can make strides in understanding and managing this complex disease.
See more about Crohn’s Disease here.
If you’re interested in learning about the 10 Most Common Diseases Affecting Humans Worldwide, click HERE.





This article is incredibly informative! As someone who has a family member with Crohn’s disease, I appreciate the detailed overview of the condition and its treatment options
Great job on this post! It’s clear and easy to understand, even for someone like me who is new to learning about Crohn’s disease
Thank you for shedding light on such an important topic. I found the section on prevention particularly helpful and will be sharing this article with friends and family.
As a healthcare professional, I can attest to the accuracy and thoroughness of this article. Well done!
I’ve been living with Crohn’s disease for years, and this article provided me with new insights and information. Thank you for raising awareness about this condition..
Jake Smith (jake.smith@example.com): “Hey, great article! I’ve been dealing with Crohn’s for a while now, and your post really hit home. Keep up the good work!”
This is exactly what I needed! Your article is so well-researched and informative. Thanks for sharing your knowledge with us!